12 Bird similar to nuthatch: You can see
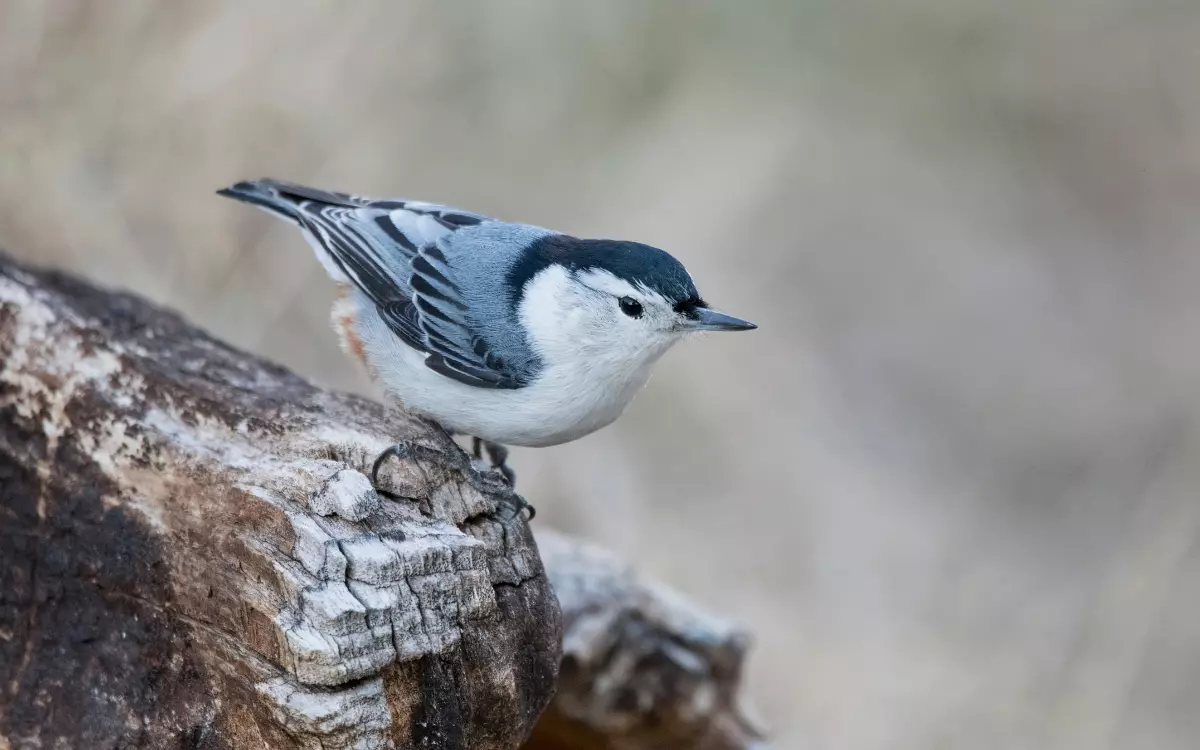

Here we are collected exactly 8 birds that simlilar to nuthatch and create a shorts notes at first that also help you to understand their species, colour , behavior and habitas.
Nuthatches are small, agile birds known for their ability to climb down trees headfirst. They have a compact build, with short tails and long, strong bills. Nuthatches are usually gray or blue on top and white or pale underneath. They are often found in wooded areas, making their homes in tree trunks or branches.
In one table all informatin about 7 birds similar to nuthatch :
| Species | Description | Behavior | Habitat | Similarities and Differences with Nuthatches |
| Chickadee | Black cap and bib, white cheeks, grey wings and back | Friendly, curious, adaptable | Various environments, including backyard feeders | Different social behavior, often forming small flocks |
| Treecreeper | Camouflaged plumage, slender, down-curved beak | Specialized climbing abilities | Woodlands and forests | Treecreepers move upwards, while nuthatches can go up and down |
| Wren | Tiny bird, brown barred feathers, powerful song | Energetic, incessant foraging | Gardens and woodlands | Wrens hop around in the underbrush, while nuthatches climb tree trunks |
| Bushtit | Small size, long tail, grey-brown color | Social, acrobatic, builds spherical nests | Woodlands and scrublands in western North America | More social, found in groups, and have longer tails |
| Marsh Wren | Small size, long tail, brown upper parts with white throat and belly | Non-migratory, forms large winter flocks | Fresh and saltwater marshes | Associated with wetlands, while nuthatches are found in wooded areas |
| Red-breasted Nuthatch | Bold white eyebrow, prefers coniferous forests | Acrobatic, attracted to feeders with sunflower seeds, peanuts, and suet | Coniferous forests in the United States | Uses conifer tree resin to defend nest cavity |
| Brown-headed Nuthatch | Brown cap, blue-gray upperparts, white underparts | Social, helpers from previous broods assist in raising the next | Pine forests in the United States | Uses tools for foraging |
| Tufted Titmouse | Gray upper body, white front, a tuft on its head | Curious, bold, often found at feeders | Deciduous and mixed forests, backyards | Similar foraging behavior but has a crest on its head |
Nuthatch Birds overview:

Call:-
Physical Characteristics
Nuthatches are pretty cool looking! They are small and have short tails, a strong bill, and powerful legs. Their body is covered in soft feathers, which are usually grey or blue on top and lighter on the bottom. This cute appearance makes them easy to love!
Habitat and Geographical Distribution
Where can you find a nuthatch? These birds love wooded areas. They are comfortable in forests, parks, and even gardens where there are plenty of trees. Nuthatches can be found in different parts of the world, including North America, Europe, and Asia. They have various homes because they can adapt to different environments.
Behavior and Feeding Habits
What do nuthatches like to do? They are super active and busy birds! Nuthatches are excellent at climbing trees. They search for food in the bark, looking for insects and seeds to eat.
They have a special way of storing their food in tree bark to eat later when they are hungry. Nuthatches also have strong voices and make a variety of sounds to communicate.
In this section, we learned about the physical characteristics, habitat, and behavior of the nuthatch. Understanding these aspects helps us see why they are unique and allows us to compare them with other birds more easily.
Understanding the Nuthatch
Nuthatches are amazing birds that are fun to watch and learn about. Let’s get to know them better by looking at their physical characteristics, where they live (habitat), and how they behave and eat (feeding habits).
Physical Characteristics
Nuthatches are not very big; they are small, cute birds. They have strong, short legs that help them walk and climb trees easily. Their bodies are usually grey or blue-grey, and they have a black stripe that runs across their eyes, almost like a superhero mask!
Habitat and Geographical Distribution
Nuthatches love places with lots of trees. You can find them in forests, parks, and even in big gardens. They are happy in different parts of the world, including North America, Europe, and Asia. So, they have many places where they feel at home.
Behavior and Feeding Habits
Nuthatches are quite busy and active. They spend a lot of time climbing trees, going up and down, looking for food. They eat insects and seeds, and they are clever about saving their food for later.
They hide their food in the bark of trees, so they can find it when they are hungry. Nuthatches make different sounds, almost like they are talking or singing, which makes them interesting to listen to.
Getting to know the nuthatch helps us understand why they are special. It also helps us see how they are similar or different from other birds. Now that you know more about them, you might enjoy watching nuthatches even more!
List of 9 Bird similar to nuthatch:
1. Tufted Titmouse
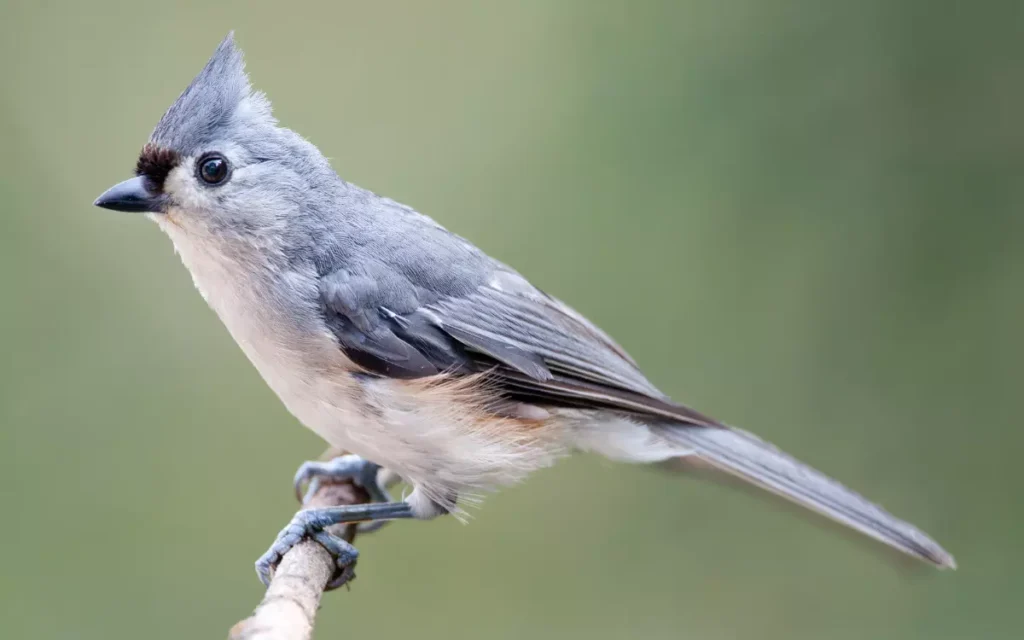

The Tufted Titmouse is an endearing bird with a distinctive gray upper body and a white front, accentuated by a noticeable tuft on its head. Its large eyes and lively demeanor make it a favorite among birdwatchers.
Behavior: These birds are known for their curiosity and boldness. They are often seen at bird feeders, where they are unafraid to take their time selecting the perfect seed. Their sociable nature is also evident as they join mixed flocks in the winter, adding a lively presence to the group.
Habitat: Tufted Titmice are found in a variety of wooded habitats, including deciduous and mixed forests. They also adapt well to suburban areas, making them a common sight in backyards with trees and bird feeders.
Unique behaviors: The Tufted Titmouse has a remarkable memory for food locations. It caches food for later consumption, remembering where it stored seeds and other food items. This ability to recall food sources is a vital survival skill, especially during the harsh winter months.
- Length: 5.5 – 6.3 in (14 – 16 cm)
- Weight: 0.63 – 0.92 oz (18 – 26 gm)
- Wingspan: 9.1 – 10.6 in (23 – 27 cm)
2. Loggerhead Shrike
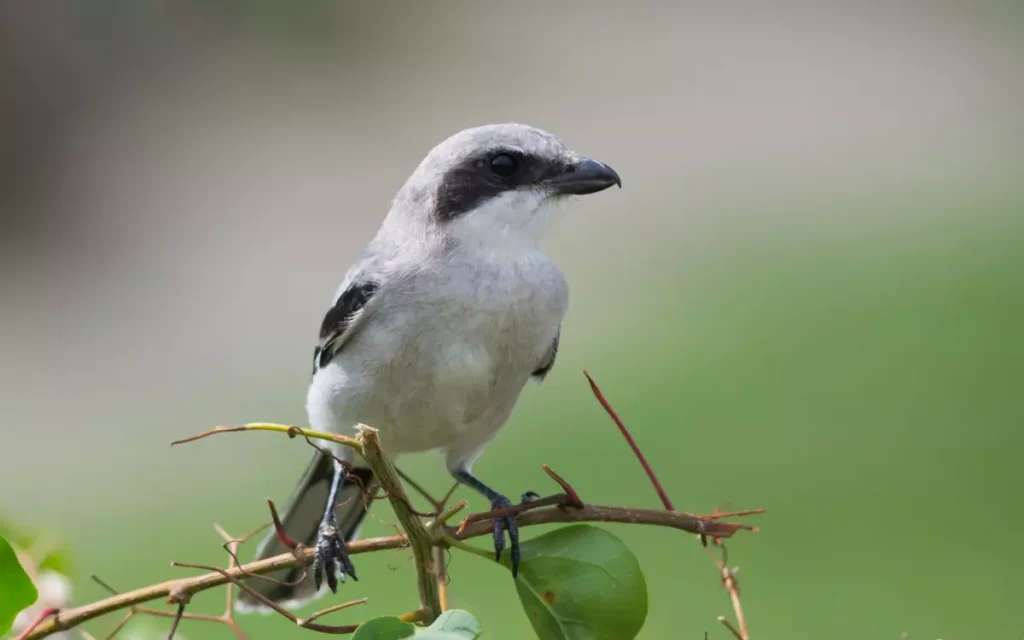

The Whistler bird is renowned for its melodious calls that resonate through the forests and woodlands where it resides. Adorned in a cloak of colorful feathers, the Whistler enchants bird enthusiasts with its harmonious tunes and vibrant presence.
These birds are not only masters of song but also contribute to the ecological balance of their habitats, making them a fascinating subject for nature lovers and conservationists who appreciate the beauty and diversity of our planet’s avian life.
- Length: 7.9-9.1 in (20-23 cm)
- Weight: 1.2-1.8 oz (35-50 g)
- Wingspan: 11.0-12.6 in (28-32 cm)
3. Chickadee
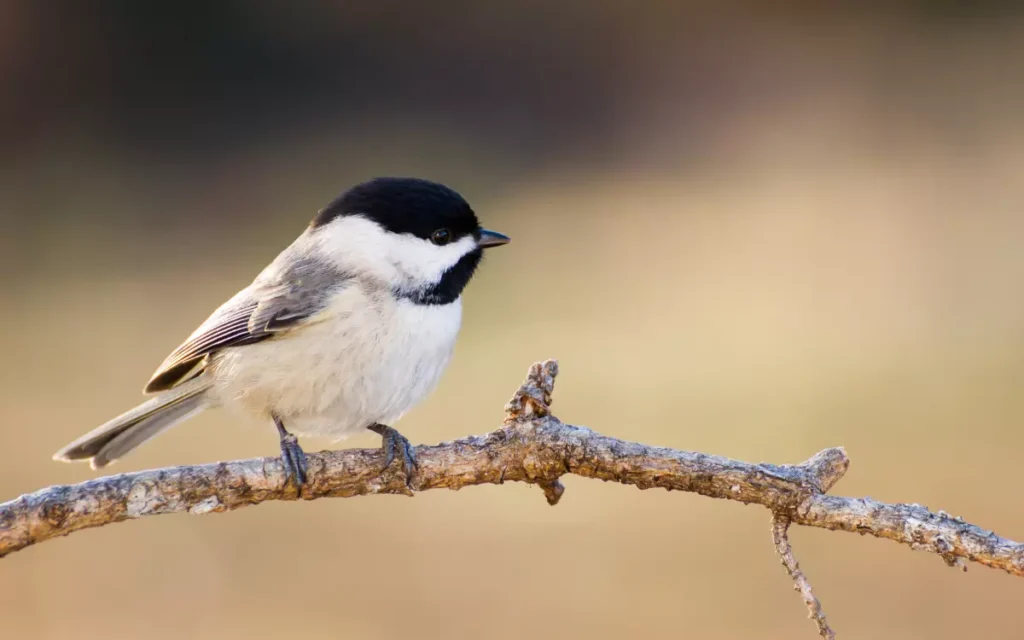

Chickadees are small birds with a distinctive black cap and bib, white cheeks, and grey wings and back. They are easily recognizable by their appearance.
Behavior: Chickadees are known for being friendly and curious. They are adaptable birds that can thrive in various environments. They often visit backyard feeders and are not shy around humans.
Habitat: Chickadees can be found in different environments, ranging from forests to urban areas. They are common visitors to backyard feeders, where they enjoy seeds and insects.
Similarities and differences with nuthatches: Like nuthatches, chickadees are small birds that are often seen climbing on trees. However, chickadees have a different color pattern and are more social, often seen in small flocks. Nuthatches have a more solitary behavior and a unique ability to climb down trees headfirst, which chickadees do not exhibit.
- Length: 4.5 – 5 in (11 – 13 cm)
- Weight: 0.3 – 0.5 oz (8 – 14 gm)
- Wingspan: 6.3 – 8.3 in (16 – 21 cm)
4. Treecreeper
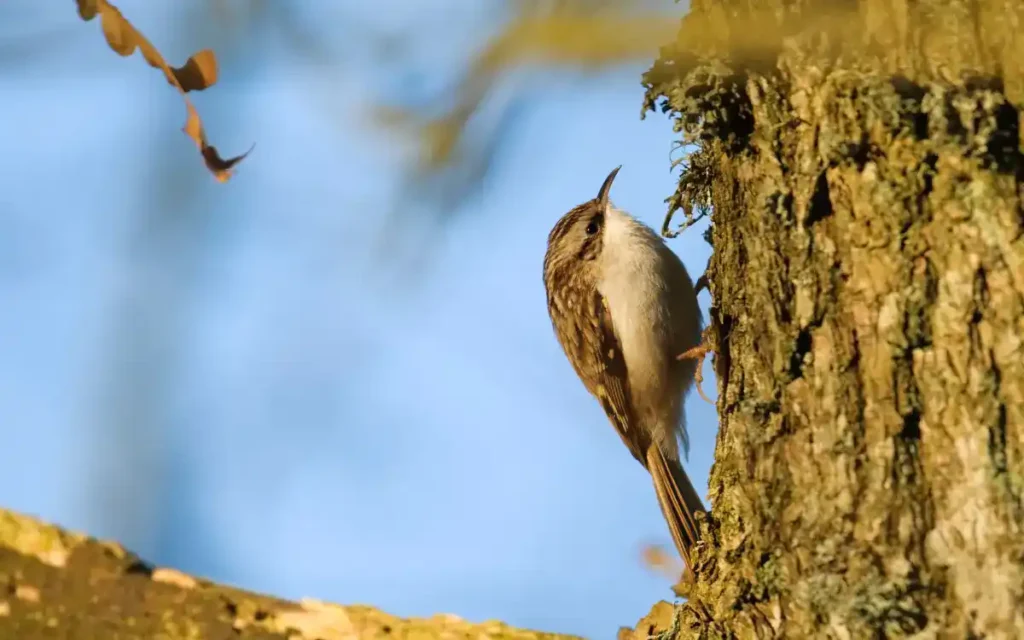

Treecreepers are birds with unique, camouflaged plumage that helps them blend into tree bark. They have a slender, down-curved beak that is perfect for picking insects out of cracks in the bark.
Behavior: Treecreepers are known for their specialized climbing abilities. They move up tree trunks in a spiral pattern, using their stiff tail feathers for support.
Habitat: Treecreepers are usually found in woodlands and forests, where there are plenty of trees for them to climb and find food.
Similarities and differences with nuthatches: Treecreepers and nuthatches both climb trees, but treecreepers usually move upwards, while nuthatches can go up and down. Treecreepers have more camouflaged feathers, helping them blend in with the bark.
- Length: 4.7 – 5.5 in (12 – 14 cm)
- Weight: 0.25 – 0.42 oz (7 to 12 gm)
- Wingspan: 6.7 – 8.3 in (17 – 21 cm)
5.Wren
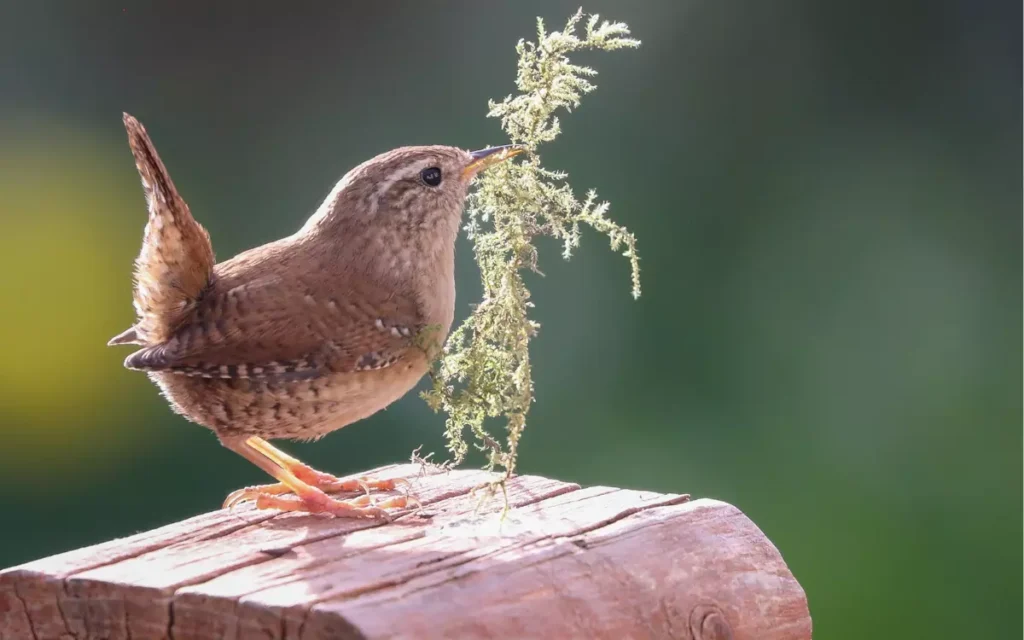

Wrens are tiny birds with brown barred feathers and a surprisingly powerful song. Despite their small size, they can fill the air with their loud and melodious tunes.
Behavior: Wrens are energetic birds that are constantly on the move, foraging for insects and spiders. They are known for their quick movements and busy nature.
Habitat: Wrens can be found in a variety of habitats, including gardens, woodlands, and hedgerows. They often nest in dense vegetation or crevices in walls.
Similarities and differences with nuthatches: While both wrens and nuthatches are small and have similar feeding habits, wrens do not climb trees in the same way as nuthatches. Wrens are more likely to hop around in the underbrush, while nuthatches are known for their ability to climb up and down tree trunks.
- Length: 3.5 – 4.3 in (9 – 11 cm)
- Weight: 0.28 – 0.46 oz (8 – 13 gm)
- Wingspan: 5.1 – 6.7 in (13 – 17 cm)
6. Brown-headed Nuthatch
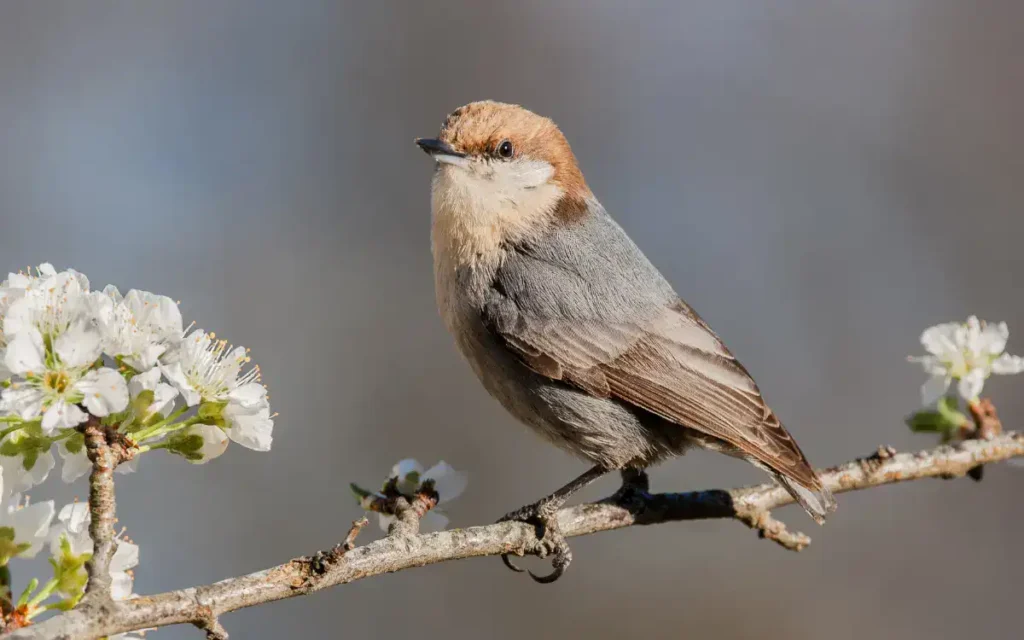

The Brown-headed Nuthatch is a small bird with a distinctive brown cap on its head. It has blue-gray upper parts and white under parts, making it a pretty sight in the pine forests where it lives.
Behavior: These birds are known for their social nature. They often have helpers from previous broods who assist in raising the next generation. This teamwork helps ensure the survival of their young.
Habitat: Brown-headed Nuthatches are primarily found in pine forests in the United States. They are particularly associated with mature pine trees, where they can find plenty of food and nesting spots.
Unique behaviors: A fascinating behavior of the Brown-headed Nuthatch is its use of tools for foraging. They are known to use small pieces of bark to pry up other pieces of bark, revealing hidden insects underneath. This clever use of tools is not common among birds and showcases their intelligence .
- Length: 3.5 – 4.3 in (9 – 11 cm)
- Weight: 0.35 – 0.42 oz (10 – 12 gm)
- Wingspan: 6.3 – 7.1 in (16 – 18 cm)
7. Pygmy Nuthatch
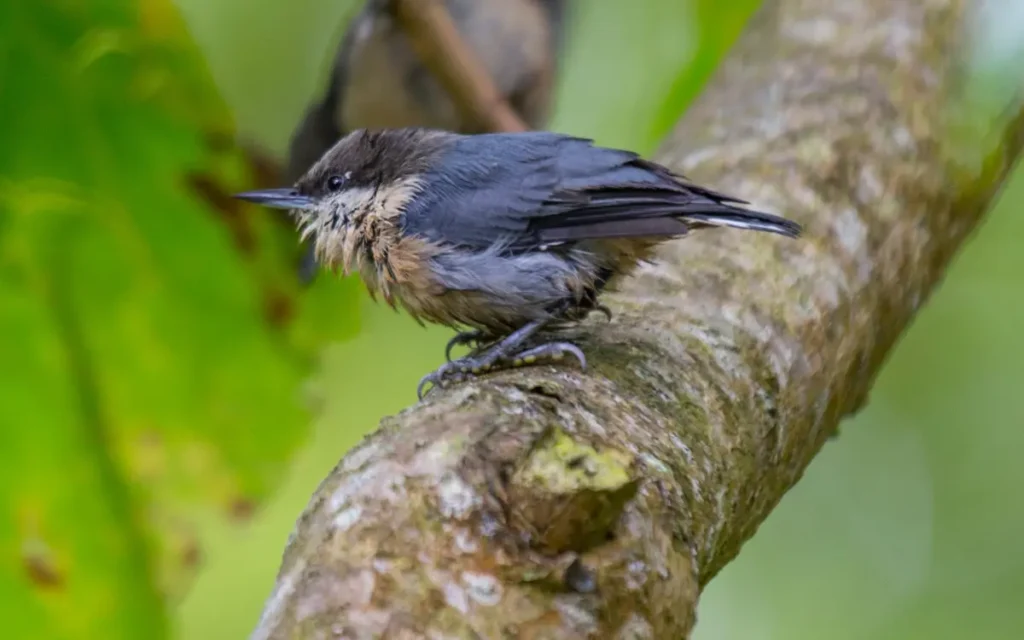

The Pygmy Nuthatch is a tiny, cute bird with soft, grey and brown feathers. It loves to play and hang around in pine trees, searching for small bugs and seeds to eat.
Even though it’s small, the Pygmy Nuthatch has a big, cheerful voice that makes the forest sound happy. It likes being with other birds, making the woods feel like a busy, fun place full of life and bird songs.
- Length: 3.5-4.3 in (8.9-10.9 cm)
- Weight: 0.3-0.4 oz (8.5-11.3 g)
- Wingspan: 7.8 in (19.7 cm)
8.Vireo
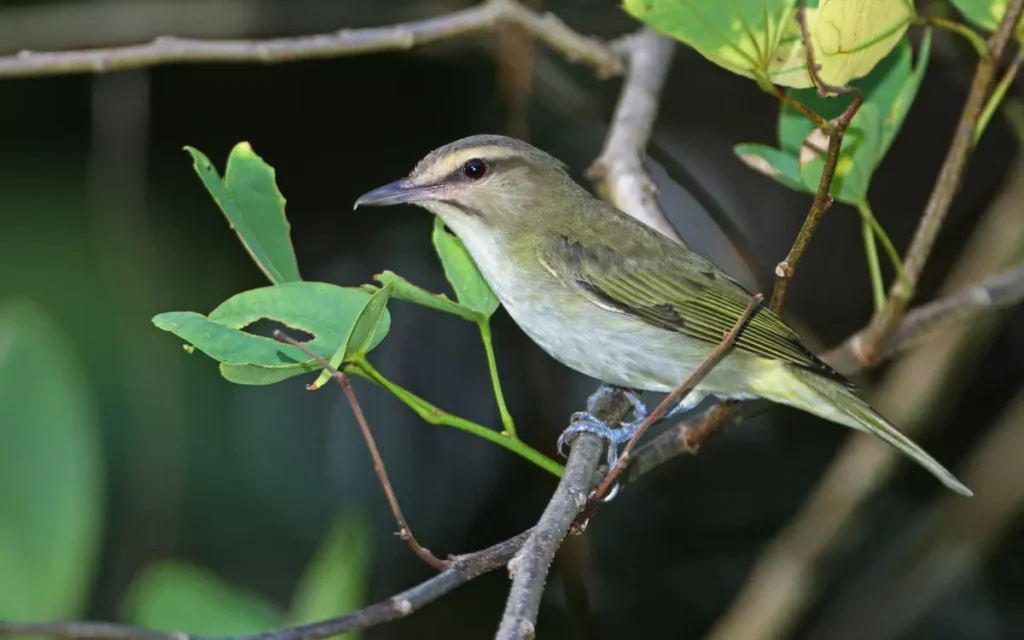

The Vireo is a small, graceful bird that fills the air with sweet songs. With its sharp eyes, it searches for insects and berries to eat among the leaves. The Vireo has lovely greenish-grey feathers that help it blend in with the trees, making it a little hard to spot.
These birds make the outdoors feel magical with their beautiful melodies, turning a walk in nature into a delightful concert of their lively tunes.
- Length: 4.7-5.1 in (12-13 cm)
- Weight: 0.4-0.9 oz (12-26 g)
- Wingspan: 9.1-9.8 in (23-25 cm)
9. Black-and-white Warbler
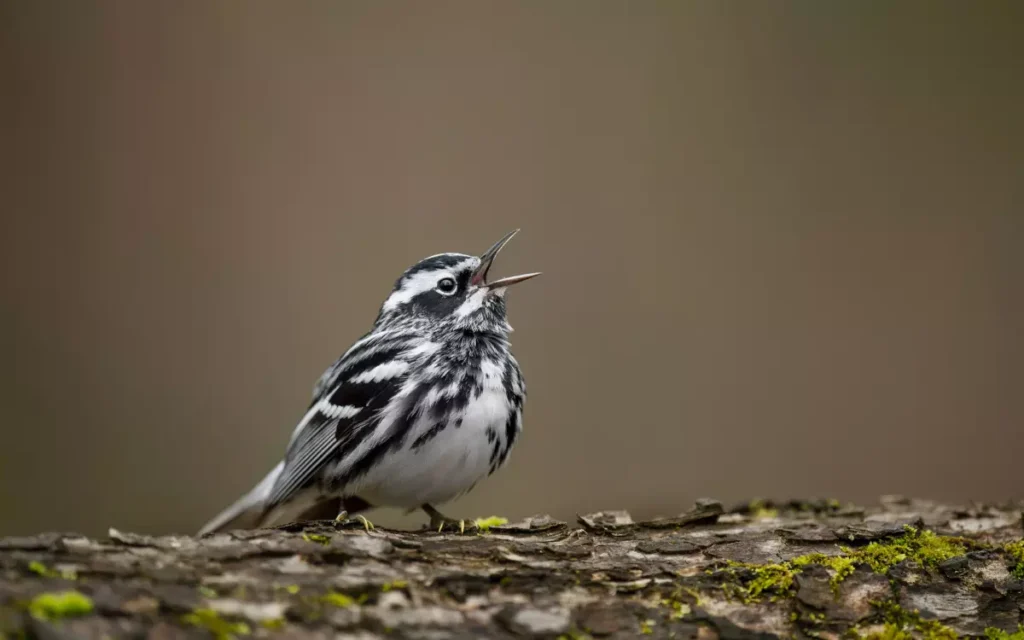

The Black-and-white Warbler is a cool bird with feathers that look like they were painted with black and white stripes. This bird loves to climb trees, looking for bugs to eat, and it moves almost like a spider crawling up a web.
Their sweet songs make the forest sound like a beautiful music show. If you see one, it’s like finding a hidden treasure because their colors make them special among other birds.
- Length: 4.3-5.1 in (11-13 cm)
- Weight: 0.3-0.5 oz (8-15 g)
- Wingspan: 7.1-8.7 in (18-22 cm)
10.Bushtit
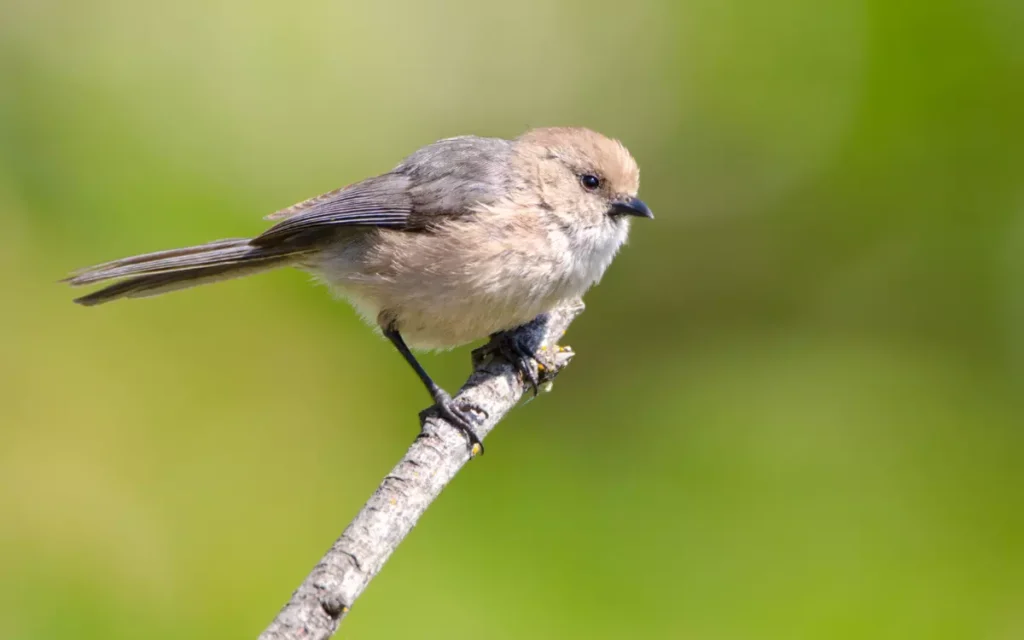

Bushtits are small birds with a long tail and grey-brown color. They are one of the tiniest birds in North America, but they are full of energy.
Behavior: Bushtits are social birds that are often seen in flocks. They are acrobatic and can hang upside down from branches while foraging for food. They build unique, spherical nests made of moss and spider webs.
Habitat: Bushtits are found in woodlands and scrublands in western North America, from Alaska to Mexico. They like areas with lots of trees and shrubs.
Similarities and differences with nuthatches: Bushtits and nuthatches are both small and enjoy eating insects. However, bushtits are more social and usually found in groups, while nuthatches are often seen alone or in pairs. Bushtits have longer tails and don’t climb trees in the same way as nuthatches .
- Length: 3.9 – 4.3 in(10 – 11 cm)
- Weight: 0.18 – 0.21 oz (5 – 6 gm)
- Wingspan: 6.3 – 7.1 in(16 – 18 cm )
11.Marsh Wren
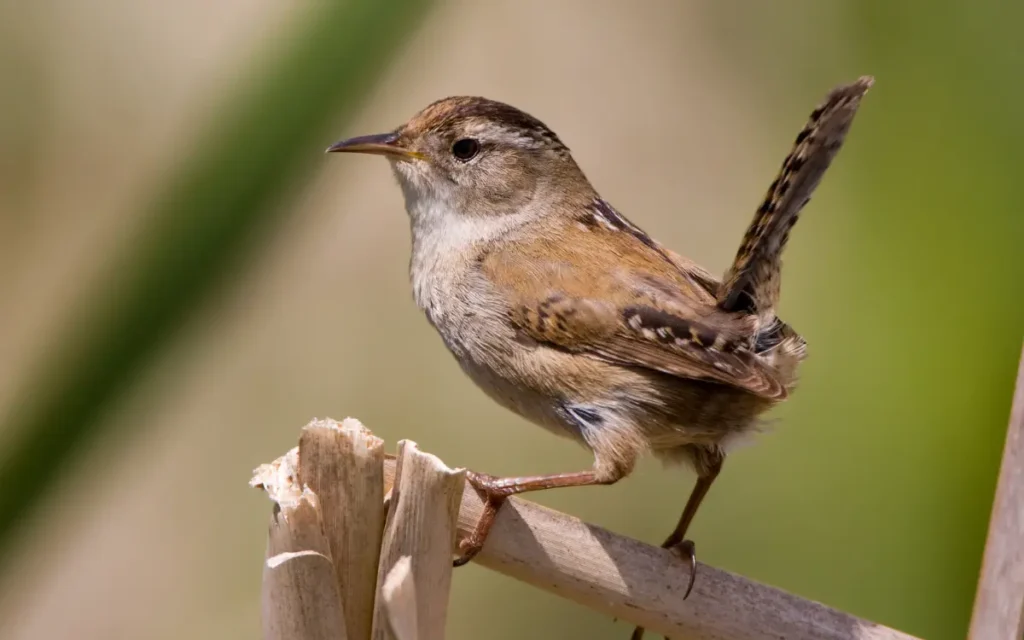

Marsh Wrens are small birds with a long tail that is often held upright. They have brown upper parts and a white throat and belly, making them well-suited to their marshy habitats.
Behavior: These birds are not known to migrate and tend to stay in their marshy homes year-round. In winter, they can form large flocks, providing warmth and safety in numbers.
Habitat: As their name suggests, Marsh Wrens are found in fresh and saltwater marshes. They thrive in areas with dense vegetation near water.
Similarities and differences with nuthatches: Marsh Wrens and nuthatches are both small, insect-eating birds. However, Marsh Wrens are more associated with wetlands, while nuthatches are typically found in wooded areas. Marsh Wrens also have a more pronounced tail and a different social structure, often forming large groups in the winter.
- Length: 3.9 – 5.5 in (10-14 cm)
- Weight: 0.3 – 0.5 oz (9-14 gm)
- Wingspan: About 5.9 in (15 cm)
12.Red-breasted Nuthatch
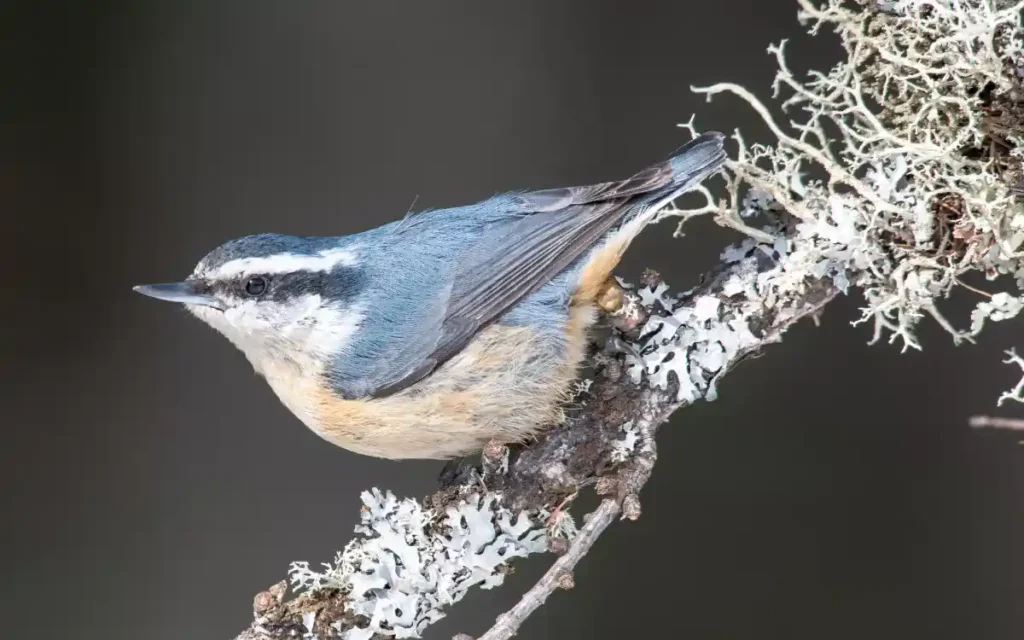

The Red-breasted Nuthatch is a small bird with a distinctive white eyebrow, making it easy to spot. They love living in coniferous forests, surrounded by pine trees.
Behavior: These birds are known for their acrobatic skills, often seen hanging upside down on tree trunks. They are drawn to feeders filled with sunflower seeds, peanuts, and suet, making them frequent visitors in backyards.
Habitat: You can find Red-breasted Nuthatches mainly in coniferous forests across the United States. They thrive in areas rich in pine trees.
Unique behaviors: A fascinating behavior of the Red-breasted Nuthatch is how they protect their nest cavity. They apply conifer tree resin around the entrance to create a sticky barrier, which helps deter predators.
- Length: 3.9 – 4.7 in (10 – 12 cm)
- Weight: 0.32 – 0.42 oz (9 – 12 gm)
- Wingspan: 7.1 – 7.9 in (18 – 20 cm)
Nesting and Breeding Habits of Nuthatches and Similar Species:
Birds have various nesting and breeding habits, and nuthatches are no exception. Let’s take a closer look at how nuthatches and some similar species go about creating their homes and raising their young.
Nuthatches:
- Nest in cavities: Nuthatches typically nest in cavities, which can be natural holes in trees or those previously used by other birds, such as woodpeckers.
- Use of abandoned woodpecker nests: Some nuthatch species are known to appropriate abandoned woodpecker nests, making them their own. They may also use nest boxes if available.
- Nesting materials: Inside the cavity, nuthatches line their nests with soft materials like feathers, fur, or bark strips to create a cozy environment for their eggs and chicks.
Similar Species:
- Variations in nesting habits: Different species have unique nesting habits. For example, rock nuthatches build their nests out of mud, plastering it onto rock crevices. They often decorate the outside of their nests with stones or other materials.
- Tufted Titmouse: This species nests in tree cavities or nest boxes, lining the nest with soft materials like hair, fur, or moss.
- Brown Creeper: Unlike nuthatches, Brown Creepers build their nests behind loose bark on tree trunks, creating a hammock-like structure with twigs, bark, and spider webs.
Know more about – Nuthatch full information
Conservation Status and Challenges:
The conservation status of nuthatches and similar species is a topic of concern for bird enthusiasts and conservationists alike. While some species are thriving, others face significant challenges that could threaten their future.
Conservation Status:
- Nuthatches: Most nuthatch species are currently classified as Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). However, this does not mean they are free from threats. Some species, like the Brown-headed Nuthatch, have specific populations that are declining due to habitat loss.
Challenges Faced by These Birds:
- Habitat Loss: One of the biggest threats to nuthatches and similar species is the loss of their natural habitats. Deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion all contribute to the reduction of suitable living spaces for these birds.
- Climate Change: Changing climate patterns can disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems, affecting the availability of food and nesting sites for nuthatches and other birds.
- Pesticides and Pollution: The use of pesticides in agriculture can poison the insects that many of these birds rely on for food. Pollution also poses a threat to their health and habitats.
- Competition and Predation: In some areas, nuthatches and similar birds face competition from invasive species for food and nesting sites. Predation by domestic cats and other animals is also a concern.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between a nuthatch and a creeper?
Ans: Nuthatches can climb down trees headfirst, while creepers typically spiral upwards. Nuthatches have a more robust body and shorter tail, whereas creepers have a slender body and a longer tail.
Q: What is the difference between a nuthatch and a red-breasted nuthatch?
Ans: The main difference is in their coloring. Red-breasted nuthatches have a distinct red or chestnut-colored breast, while other nuthatches, like the white-breasted nuthatch, have a white breast.
Q: How do you identify a nuthatch?
Ans: Nuthatches are small birds with a compact build, short tails, and long bills. They often have a distinctive coloring pattern, with gray or blue on top and white or pale underneath.
Q: What is the nickname of the nuthatch?
Ans: Nuthatches are sometimes called “upside-down birds” because of their unique ability to climb down trees headfirst.
Q: Is a nuthatch a finch?
Ans: No, nuthatches are not finches. They belong to the family Sittidae, while finches belong to the family Fringillidae.
Q: What are the relatives of the nuthatch?
Ans: Close relatives of the nuthatch include the titmice and chickadees, which are also small, tree-climbing birds that share similar habitats and behaviors.
Conclusion:
Birds similar to nuthatches, such as chickadees, treecreepers, and wrens, offer a delightful view into the variety of avian life. These small, agile creatures, with their unique behaviors and habitats, remind us of the importance of maintaining their natural environments.