Robin vs Blue Jay:Differences
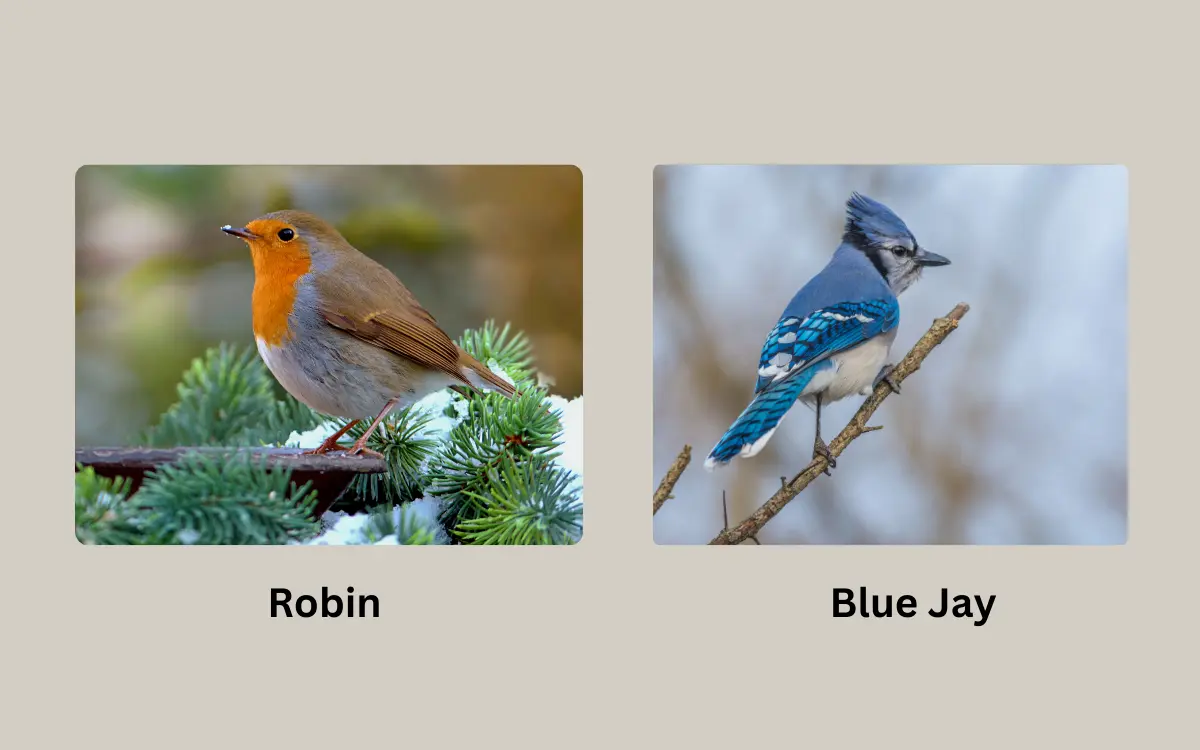

In the avian world, the comparison of Robin vs Blue Jay offers a captivating insight into their distinct behaviors, habitats, and vocal patterns.
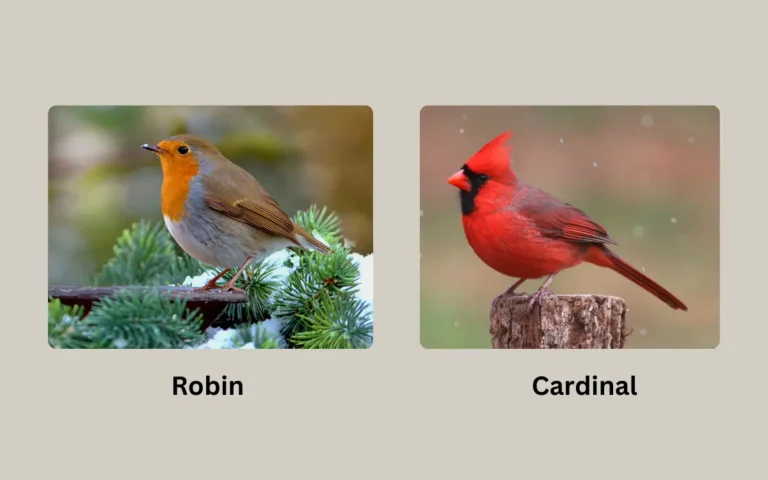
Robin vs. Blue Jay: Similarities and Differences
Have you ever watched birds in your backyard and wondered about their lives? Let’s explore two fascinating bird species: the Robin and the Blue Jay. These birds are quite different, but they also share some similarities. Understanding these can teach us a lot about bird behavior and nature.
Key Differences Between Robin and Blue Jay:
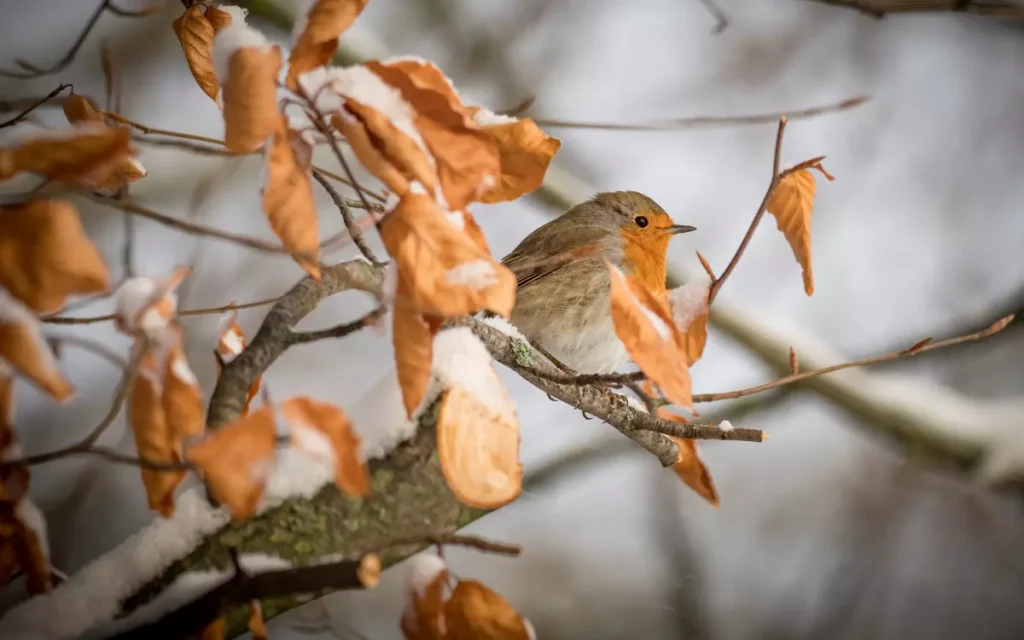

Robins call
- Wingspan:14 3/4 – 16 1/2 inches
- Weight:64.8 – 84.2 grams, or 2 1/3 – 3 ounces
- Nest Location: Nests are commonly found 5 to 15 feet above ground, in dense bushes or trees
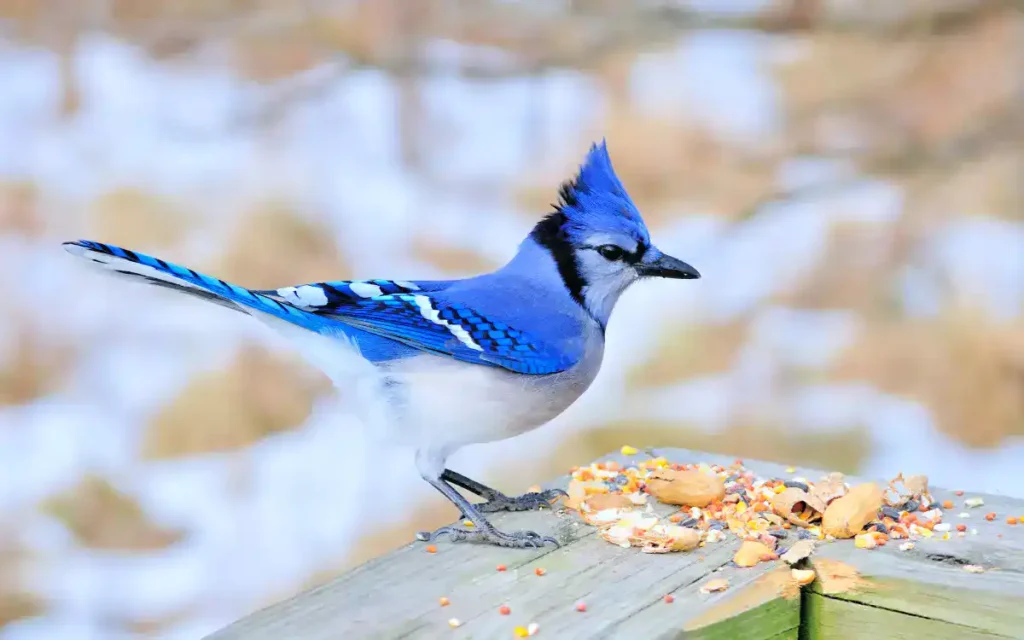

Blue Jay call
- Wingspan:34 – 43 cm (13 – 17 in)
- Weight:70 – 100 grams (2.5 – 3.5 oz)
- Nest Location:Nests are typically located in trees, 5 to 15 feet above ground
Vocalization
Robins and Blue Jays have distinct vocalizations. The Blue Jay is known for its loud and piercing call, while the Robin sings a soft and melodious tune. This difference in their songs is not just about sound; it reflects their unique behaviors and habitats.
Coloration
When it comes to coloration, these birds are quite the artists of nature. The Blue Jay sports bright blue and white feathers, making it a vibrant sight. The Robin, on the other hand, is known for its rust-colored breast and grayish-brown back, a more subtle but equally beautiful combination.
Learning Abilities
Learning abilities vary between these two species. Blue Jays are known for their intelligence and adaptability, often learning to mimic the sounds of other birds. Robins, while also smart, show their intelligence more in their foraging habits and nest building.
Distinctive Markings
Each bird has its own distinctive markings. The Blue Jay’s notable feature is its crest, a pointy set of feathers on top of its head. The Robin is easily recognized by its colorful breast, a standout feature among birds.
Mimicry
The Blue Jay has a unique skill of mimicry, especially imitating the calls of hawks. This clever tactic is used to scare away potential threats or competitors, showcasing the bird’s adaptability and intelligence.
Feeding Habits
Their feeding habits are quite different. The Blue Jay’s omnivorous diet includes seeds, nuts, and even small animals. In contrast, the Robin prefers a diet rich in insects and berries, making it more of a specialist in its food choices.
Nesting Preferences
Nesting preferences also differ. Blue Jays tend to build their nests in trees or bushes, while Robins often construct theirs on ledges, eaves, or branches. This choice of nesting location reflects their adaptation to different environments.
Nesting Material
In terms of nesting materials, both birds use twigs, grass, and mud, but their nest structures can be quite distinct, reflecting the differences in their nesting preferences.
Territorial Behavior
The Blue Jay is known for its territorial behavior, especially during the nesting season. They can be quite protective of their space, often defending their nests vigorously.
Migration Patterns
Their migration patterns are another point of distinction. While Robins migrate to warmer areas during winter, Blue Jays tend to stay in the same area throughout the year.
Behavior in Winter
In winter, each bird adapts differently. Robins might migrate or change their feeding habits, while Blue Jays often stay put and may gather in groups.
Social Behavior
The social behavior of these birds varies. Blue Jays can be quite aggressive, especially in defending their territory, while Robins are generally more sociable and less prone to territorial disputes.
Song Complexity
When it comes to song complexity, both birds have a range of calls and songs, but the Blue Jay’s ability to mimic other birds adds an extra layer to its vocal repertoire.
Eating Preferences
Eating preferences of these birds reflect their habitats and feeding strategies. Robins, with their preference for earthworms and insects, are often seen hopping on the ground, while Blue Jays are more versatile, eating a variety of foods including nuts and seeds.
Size
In terms of size, Blue Jays are generally larger than Robins, with a more robust build and longer tail.
Range
The range of these birds is quite extensive. Robins are found across North America, while Blue Jays are typically seen in forests and woodlands in North America.
Nesting Season
The nesting season also shows variation. Robins generally nest from spring to early summer, aligning with the availability of insects. Blue Jays, on the other hand, start nesting in spring and can extend into mid-summer.
Egg Color
There’s a notable difference in egg color as well. Blue Jay eggs are pale blue or green with brown speckles, whereas Robin eggs are famously bright blue.
Parental Care
Both species exhibit strong parental care, with both male and female birds participating in nest building, incubating eggs, and feeding chicks.
Mobility
The mobility of Robins is particularly noticeable. They are often seen hopping on the ground, which is their way of foraging for insects and worms.
Intelligence
In terms of intelligence, both birds exhibit problem-solving skills, though Blue Jays are particularly noted for their clever behaviors like mimicry and using tools.
Predator Imitation
The predator imitation skill of the Blue Jay, particularly mimicking the call of hawks, is a remarkable example of their adaptability and intelligence.
Winter Adaptations
Both birds have winter adaptations. Robins may migrate or change their food sources, while Blue Jays typically stay in the same area, forming groups to keep warm.
Urban Adaptability
Both species have adapted well to urban environments. Robins are often seen in parks and gardens, while Blue Jays can also thrive in city settings, utilizing food sources and nesting spots in these areas.
Egg Clutch Size
In terms of egg clutch size, Blue Jays lay anywhere from 2 to 7 eggs, while Robins typically lay 3 to 4 eggs per clutch.
Lifespan
The lifespan of both birds can vary based on factors like environment and predation. Robins and Blue Jays can live several years, with some individuals living much longer under ideal conditions.
Understanding these differences between Robins and Blue Jays not only enriches our birdwatching experiences but also enhances our knowledge of these fascinating creatures and their roles in the ecosystem.
Read also:
Robin vs Cardinal: Everything you need to know
Blue Jay Spiritual Meaning: Symbolism and Love Revealed
Robin Vs Blue Jay: Comparison Table
Here’s a simple table to help you understand the main differences and similarities between Robins and Blue Jays:
| Feature | Robin | Blue Jay |
| Vocalization | Soft, melodious song | Loud, piercing call; can mimic other birds |
| Coloration | Rust-colored breast, grayish-brown back | Bright blue and white feathers |
| Feeding Habits | Prefers insects and berries | Eats seeds, nuts, and small animals; omnivorous |
| Nesting Preferences | Builds nests on ledges, eaves, or branches | Prefers nesting in trees or bushes |
| Nesting Material | Uses twigs, grass, and mud | Similar, uses twigs, grass, and mud |
| Territorial Behavior | Less territorial | More territorial, especially during nesting |
| Migration Patterns | Migrates to warmer areas in winter | Generally stays in the same area year-round |
| Behavior in Winter | May migrate or change feeding habits | Stays put, often gathers in groups |
| Social Behavior | Sociable, less prone to disputes | Can be aggressive, especially in defending territory |
| Song Complexity | Clear, whistled notes | Variety of calls; complex due to mimicry |
| Eating Preferences | Forages on the ground for worms and insects | Versatile, forages on ground and in trees |
| Size | Smaller, compact body | Larger with a robust build and long tail |
| Range | Found across North America, Europe, and Asia | Mainly found in North America |
| Nesting Season | Spring to early summer | Spring to mid-summer |
| Egg Color | Light blue with no speckles | Pale blue or green with brown speckles |
| Parental Care | Both parents care for young | Similar, both parents involved |
| Mobility | Hops on the ground | Flies more, can hop and walk |
| Intelligence | Smart, especially in foraging | Highly intelligent, uses mimicry |
| Predator Imitation | Does not mimic predators | Mimics hawk calls as defense |
| Winter Adaptations | May migrate or change diet | Forms groups, stays in the area |
| Urban Adaptability | Adapts well to urban environments | Also adapts well to urban settings |
| Egg Clutch Size | 3-4 eggs per clutch | 2-7 eggs per clutch |
| Lifespan | Several years under ideal conditions | Similar lifespan |
Frequently Asked Questions :
Are robins and Blue Jays enemies?
A:No, robins and Blue Jays are not natural enemies. However, they can have territorial disputes, especially during the breeding season when both species are actively nesting and protecting their young.
Why is Robin chasing blue jay?
A: A Robin may chase a Blue Jay to defend its territory or protect its nest. Blue Jays are known to be aggressive and may pose a threat to the eggs or young of other birds, prompting the Robin to take defensive action.
Is the blue jay an aggressive bird?
A: Yes, Blue Jays are known for their aggressive behavior, particularly in terms of defending their territory or nest. They can be assertive towards other birds and even humans if they feel threatened or if their nesting area is disturbed.
Is a blue jay a cardinal?
A: No, a Blue Jay is not a Cardinal. They are different species. Blue Jays are part of the Corvidae family, known for their intelligence and bold nature, while Cardinals, known for their vivid red color, belong to the Cardinalidae family.
Conclusion:
While Robins and Blue Jays share the same environment, they are quite different. Robins are known for their melodious songs and red breasts, preferring insects and berries. Blue Jays, with their striking blue feathers, are more aggressive and have a varied diet. Both birds, each unique in behavior and appearance, add beauty and diversity to our backyards and parks.