Hummingbirds Everything Need To Know

Hummingbirds are small birds with colorful feathers and fast-flying wings. In this article we will cover everything that help you to know more about this bird.
| Category | Details |
| Classification | |
| Family | Trochilidae |
| Genera and Species | Over 300 species in 100+ genera |
| Lifespan | |
| Average Lifespan | 3 to 5 years |
| Maximum Lifespan | Up to 9 years |
| Type of Species | |
| Most Common Species | Ruby-throated Hummingbird, Anna’s Hummingbird, Rufous Hummingbird |
| Largest Species | Giant Hummingbird (Patagona gigas) |
| Smallest Species | Bee Hummingbird (Mellisuga helenae) |
| Habits | |
| Feeding | Nectar from flowers, small insects, and spiders |
| Activity | Highly active, capable of hovering and flying backward |
| Nests | |
| Nesting Material | Plant fibers, downy substances, spider silk |
| Nest Size | Small cup-shaped nests, about the size of a walnut |
| Location | Trees, shrubs, and sometimes man-made structures |
| Migration | |
| Migration Pattern | Many species migrate long distances, often from North America to Central and South America |
| Timing | Typically during spring and fall |
| Eggs | |
| Clutch Size | Usually 2 eggs |
| Egg Size | Very small, about the size of a pea |
| Incubation Period | 14-23 days |
Size and Weight
Hummingbirds are among the smallest birds, typically a few inches long and weighing 2 to 4 grams, about the weight of a penny. Their light bodies allow for amazing agility.
Beak Shape and Function
Their long, slender beaks are perfect for sipping nectar from flowers and catching small insects, essential for their diet.
Wing Structure and Flight
Hummingbirds’ wings beat up to 80 times per second, allowing them to hover, fly backward, and even upside down. This makes them unmatched in aerial abilities.
Unique Adaptations
They can hover mid-air to feed on nectar, have high metabolisms that require frequent eating, and their iridescent feathers reflect dazzling colors.
Hummingbirds’ small size, specialized beaks, powerful wings, and unique adaptations make them truly extraordinary creatures.
Habitat and Distribution
Hummingbirds thrive in diverse environments across the Americas. Here are key points about their habitat and distribution.
Geographic Range
Hummingbirds are found from Alaska to Tierra del Fuego, with the highest diversity in tropical regions like Central and South America.
Preferred Habitats
They favor forests, gardens, and meadows where flowers are abundant. They are often seen in both rural and urban areas with ample flowering plants.
Migration Patterns
Many species migrate long distances, often from North America to Central and South America, typically during spring and fall. Their migration is driven by food availability and climate changes.
Most beautiful well known Hummingbird Species
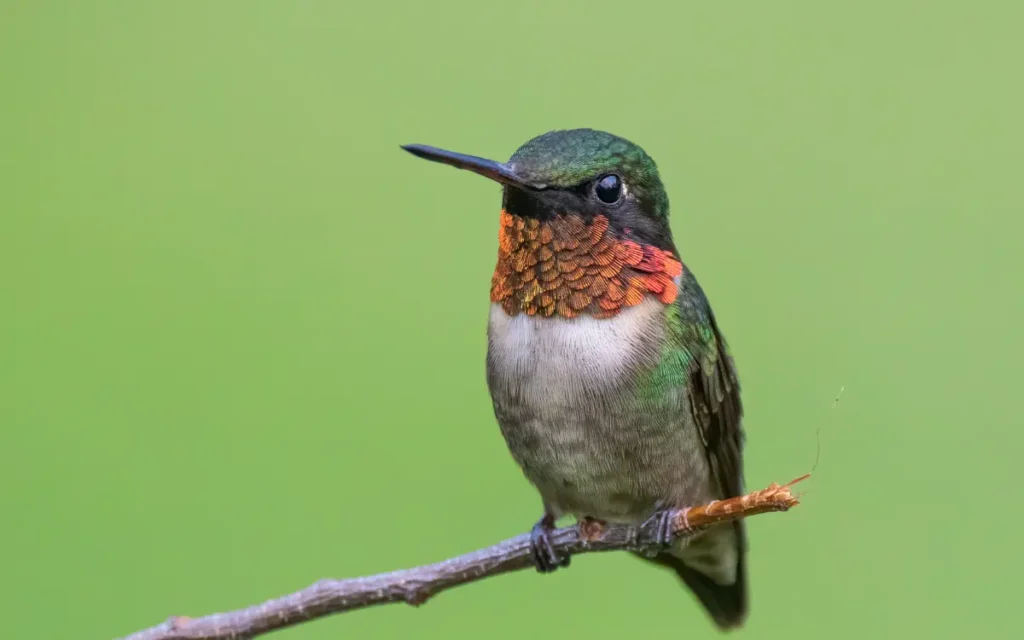
1.Ruby-throated Hummingbird

Call:-
The Ruby-throated Hummingbird is a stunning bird known for its vibrant ruby-red throat, contrasting with its green back and white underparts. These small yet remarkable birds are common in eastern North America and are celebrated for their impressive long-distance migrations and agile flight.
- Description and Identification: Green back, white underparts, and a brilliant ruby-red throat (males).
- Range and Habitat: Eastern North America to Central America; found in gardens, forests, and meadows.
- Behavior and Diet: Feeds on nectar and insects; known for long migrations.
- Length: 3-3.75 inches
- Weight: 2-6 grams
- Wingspan: 3.1-4.3 inches
- Egg Size: About 0.5 inches
- Located: Eastern US to Central America
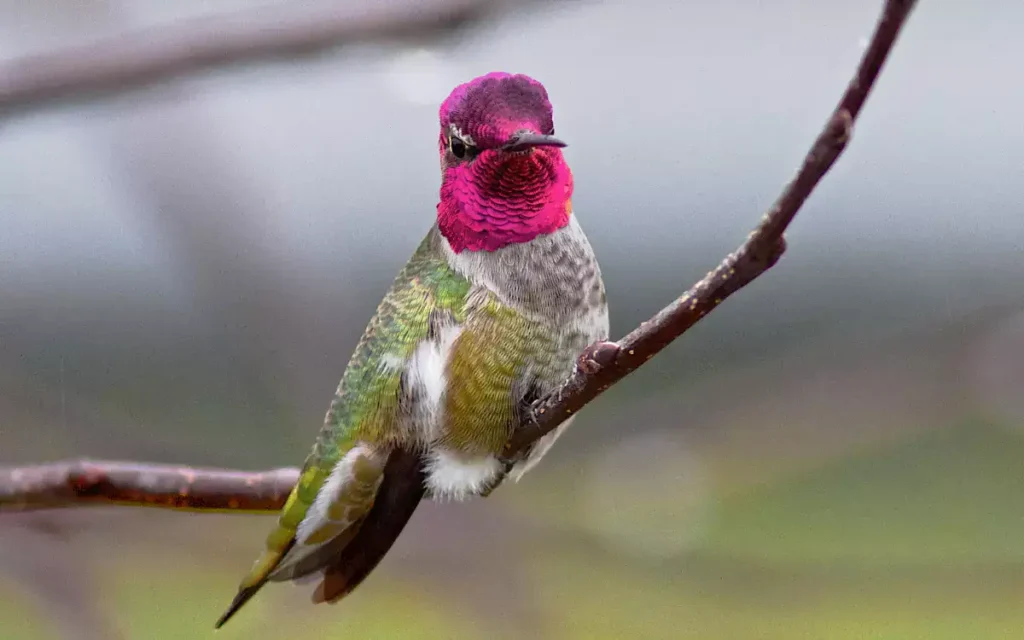
2.Anna’s Hummingbird

Calls:-
Anna’s Hummingbird is a striking species with iridescent emerald feathers and a rose-pink throat in males. Found along the West Coast of North America, these birds are well-known for their bold colors, aggressive territorial behavior, and adaptability to various habitats, from gardens to open woods.
- Description and Identification: Iridescent emerald feathers, rose-pink throat (males).
- Range and Habitat: West Coast of North America; gardens, parks, and open woods.
- Behavior and Diet: Feeds on nectar, insects, and spiders; aggressive territorial behavior.
- Length: 3.9-4.3 inches
- Weight: 3-4 grams
- Wingspan: 4.7 inches
- Egg Size: About 0.5 inches
- Located: Western US and Canada
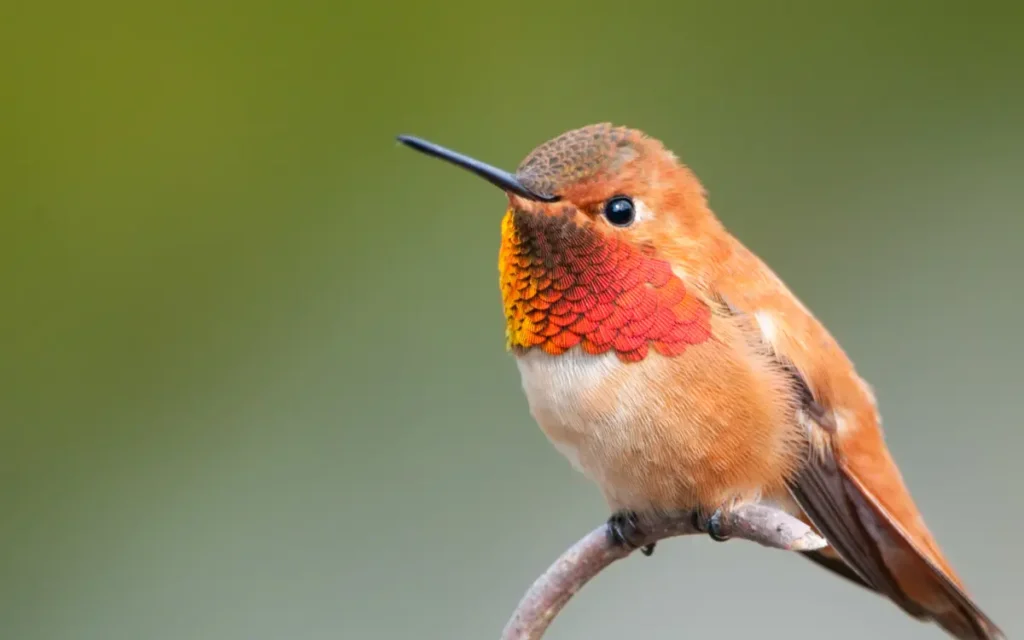
3.Rufous Hummingbird

Call:-
The Rufous Hummingbird is a bright orange jewel of the hummingbird family, with males displaying a fiery red throat. Native to western North America, these feisty birds are renowned for their aggressive nature and extensive migrations, which take them from the Pacific Northwest to Mexico.
- Description and Identification: Bright orange body, iridescent red throat (males).
- Range and Habitat: Western North America to Mexico; meadows, forests, and gardens.
- Behavior and Diet: Feeds on nectar and insects; known for its aggressive nature.
- Length: 2.8-3.5 inches
- Weight: 2-5 grams
- Wingspan: 4.3 inches
- Egg Size: About 0.5 inches
- Located: Western US to Mexico
4.Black-chinned Hummingbird

Call:-
The Black-chinned Hummingbird features a metallic green body, a distinctive black chin, and a subtle purple band on its neck. Inhabiting western North America, these birds thrive in diverse environments, including deserts and woodlands, and are known for their energetic courtship displays.
- Description and Identification: Metallic green body, black chin, and purple band on the neck (males).
- Range and Habitat: Western North America; deserts, woodlands, and gardens.
- Behavior and Diet: Feeds on nectar, insects, and spiders; performs courtship displays.
- Length: 3.5 inches
- Weight: 3-4 grams
- Wingspan: 4.3 inches
- Egg Size: About 0.5 inches
- Located: Western US and Mexico
5.Costa’s Hummingbird
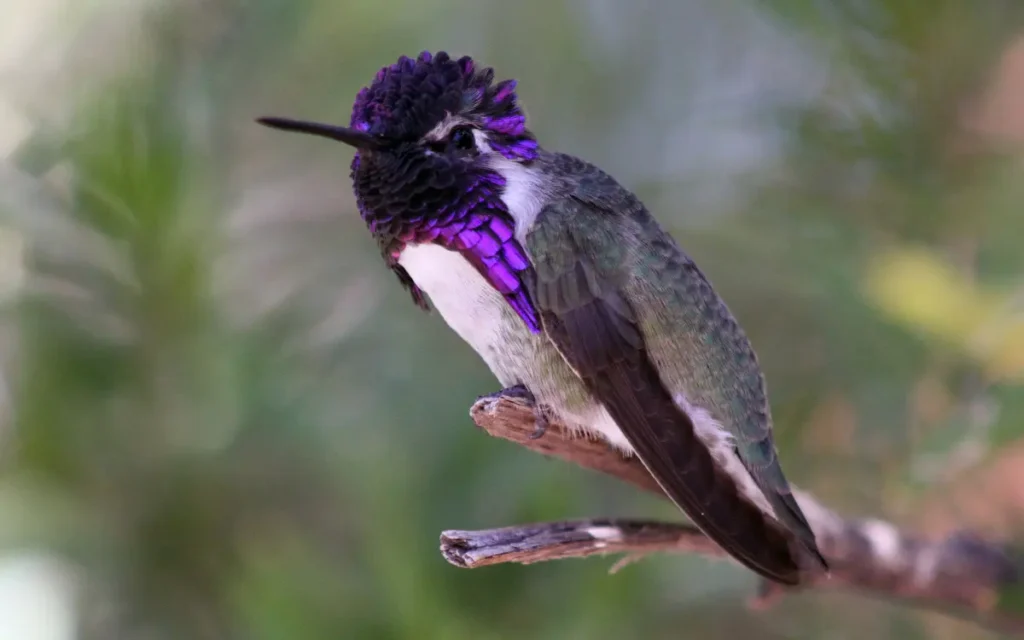

Costa’s Hummingbird is a desert specialist with a shimmering green body and a vibrant violet crown and throat in males. Found in the arid regions of the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico, these hummingbirds are admired for their ability to adapt to harsh, dry environments while maintaining their dazzling appearance.
- Description and Identification: Shimmering green body, violet crown and throat (males).
- Range and Habitat: Southwestern United States and Northwestern Mexico; deserts and arid regions.
- Behavior and Diet: Feeds on nectar and insects; adapts to arid environments.
- Length: 3-3.5 inches
- Weight: 2-3 grams
- Wingspan: 4.3 inches
- Egg Size: About 0.5 inches
- Located: Southwestern US and Northwestern Mexico
Read also:- 8 Hummingbirds Facts you should know
Feeding HabitsDetails
| Feeding Habits | Details |
|---|---|
| Types of Food | Nectar, insects, spiders |
| Feeding Mechanisms | Long beaks for nectar, rapid tongues, catching insects mid-air |
| Role in Pollination | Transfers pollen while feeding on nectar, crucial for flowers |
Reproduction and Lifespan
| Reproduction and Lifespan | Details |
|---|---|
| Mating Behaviors and Rituals | Males perform aerial displays and dives to attract females |
| Nesting Habits and Construction | Small cup-shaped nests made of plant fibers and spider silk, placed in trees or shrubs |
| Incubation Period and Care of Young | Incubation lasts 14-23 days; females care for the chicks until fledging |
| Lifespan and Survival Challenges | Average lifespan is 3-5 years; threats include predators, habitat loss, and climate change |
Conservation Status
| Conservation Status | Details |
|---|---|
| Threats to Populations | Habitat loss, climate change, predation |
| Conservation Efforts | Protected areas, habitat restoration, research programs |
| How Individuals Can Help | Plant hummingbird-friendly plants, set up feeders, support conservation organizations |
Conclusion
Hummingbirds are remarkable for their unique traits, behaviors, and role in pollination. They face threats like habitat loss and climate change. Conservation efforts and individual actions, such as planting nectar-rich flowers and using feeders, are vital for their survival.
Learn more through articles on hummingbird facts and support conservation to help these tiny wonders thrive.